Over the past few years Formula 1 has seen several changes in the rules and the teams have come up with some brilliant innovative ideas to cope up with the new regulations. There also has been significant changes with the power unit and the transmission. According to current regulations, it is mandatory for each car to have a seven speed gearbox.So, lets take a look into how these 600 bhp 1.6 litre turbcharged engines transmit the power to the wheels.
To understand better one should first know the basics of the transmission system and how the transmission works in a normal road car.
Manual Stick Shift Transmission Operation
Most of the road cars operate via a manaual stick shift gear transmission system.
Here is a basic diagram of a road car’s engine and gearbox assembly:
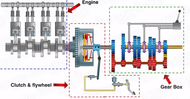
The Engine generates the power in form of rotary motion which is transmitted to the gearbox via the clutch and flywheel. Now, lets take a detail look into the power transmission.
Engine:
The power produced from the engine is converted into reciprocating motion of the piston.
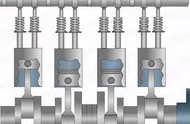
The reciprocating motion is converted into rotary motion of the crankshaft using the connecting rods.

The Rotary motion is transmitted to the flywheel, which is attached to the crankshaft output shaft.
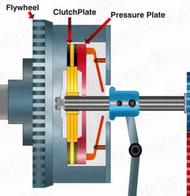
When the clutch pedal is pressed, the hydraulic pressure from the clutch reservoir forces the pressure plate to move against the rotating flywheel.
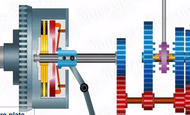
When the pedal is released the pressure plate moves toward clutch plate, and power from engine gets connected.

Gearbox:
A typical automobile gearbox consists of main shaft,lay shaft ,dog clutch and the selector mechanism.The gears on the main shaft are directly engaged to the gears on the layshaft and rotate with them.
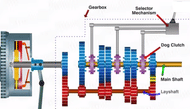
The main shaft gears do not transmit power to the main shaft, as they are mounted over the bearings.

The Power transmission is done using the dog clutches, which are directly mounted on the main shaft, and are able to move left or right, to engage with different gears on the main shaft and attain motion accordingly.

Different torque or speed variations are obtained by engaging the gears on the main shaft using the selector mechanism.
When the first gear is selected using the selector mechanism, the dog clutch shifts towards its left , engaging with the first gear. The power is thus transmitted from the gearbox input shaft tothe layshaft 1st gear, and from there to 1st gear on the main shaft and finally to gearbox output shaft.Since the diameter of the first gear is comparitively biger speed reduces, but torque is increased.

In the second gear the dog clutch moves to its right, engaging with the second gear on the main shaft, and thus another gear ratio is obtained with increase in speed and decrease in torque.
In third gear, thje second dog clutch moves to its left to mesh with the 3rd gear on the main shaft .The speed further increase with subsequent decrease in torque.To engage fourth gear the dog clutch moves to the right and meshes with the 4th gear on the main shaft.

To achieve 5th gear the third dog clutch moves to its left to mesh with with the 5th gear on the main shaft.In this highest speed is achieved, but the torque is very less.

Toe engage reverse gear, the third dog clutch moves to its right to mesh with the reverse gear on the main shaft which rotates in reverse direction using an idle gear, and thus reverse motion is transferred to the gearbox output shaft.

Differential:
The motion obtained at the gearbox output shaft through different gearing arrangements is then transferred to the differential. From the differential the power is finally transmitted to the wheels via the axle.

Sequential Gearbox System:
Modern formula 1 cars use highly automated sequential gearbox system which allows them to shift seamlessly with ease. The steering wheel on a F1 car has two gear levers, one for the upshift and the other for the downshift alongwith two clutch levers.
The clutch is needed only for the engagement of the first gear from neutral. Subsequent gears are engaged without the use of the clutch.So, what is the difference in the transmission system from a normal road car? Let’s have a look into it.
Here is a schematic diagram of the operation of the Sequential gearbox:

So, comparing the schematic with the pictures of the basic automobile transmission, you probably now have an idea of the basics of the transmission mechanism.In a sequential gearbox the main difference lies in the gear selector. The sequential gear selector and the slector shaft are the chief components in a sequential gearbox and these two components are what differentiates a sequential from a manual transmission.
When the drive upshifts or downshifts using the paddles the sequential gear (black) rotates on the red mesh, this causes the the movement of the selector forks(green) which engages the collar(similar to dog clutch) to the the gear on the main shaft.
The gear selector shaft has grooves cut on it and each selctor fork has different type of grooves cut onit. Here is the diagram showing various grooves on different selecting forks:

There is also the presence of the selector pins(blue) in the selector shaft. So, when the driver engages say reverse gear the sequential gear selector rotates which causes the selector pin to move in the grooves cut out in the selector shaft to reverse (denoted by R).
When the selector pin moves to R, it causes the movement of the selector fork and this engages the collar attached with the selector fork to reverse gear on the main shaft.Now, say when the driver engages first then the selector pin moves from R to 1 and the selector fork moves to the right engaging the collar to the first gear on the main shaft. So, this is the basic mechanism how the transmission system operates in a F1 car.
To sum it up in a nutshell the main difference in transmission mechanism between a F1 car and normal road car lies in the Sequetial Gear selector which consists of Selector shaft(Selecting forks,selecting pins and the collar). The mode of operation of these three components is what creates all the difference.
Also, in a F1 car the electronics control the clutch mechanism which in a manual transmission has to operated by the driver himself.
So, thats all about the transmission mechanism. Hope you all enjoyed it and if you have doubts please do ask.
