How big or ong is a tennis court? What are its dimensions? Let’s take a look.
The International Tennis Federation (ITF) has framed the regulations in its handbook named “Rules of Tennis“. It covers the dimensions of the tennis courts, the height of the net and the surfaces on which tennis has to be played. Tennis courts at all the tournaments and Grand Slams have to follow these rules of tennis.
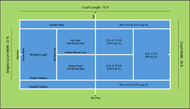
The game of tennis is played in a rectangular area, usually on a grass or clay or synthetic court. The court is 78 feet long and 36 feet wide. Additional space is provided for the players to take on the overrun balls. Including this space, the tennis court becomes 120 feet long and 60 feet wide.
A tennis court has six primary areas in it. Let us look into the size of each zone and its significance:
1. The net: The net is made of a material called twisted polyethylene and is stretched across the full width of the court. It is parallel to the baselines and divides the court into two equal halves. The net is 3 feet 6 inches high at the posts and 3 feet high in the centre. The net posts are 3 feet outside the doubles court on each side. For a singles match the net is 3 feet outside the singles court on each side.
2. Baseline: This is the line from where a serve is initiated. It is 39 feet away from the net.
3. Service area: The service area is the area which a ball has to be served into. This is a 21 x 27 (sq. feet) area divided into two – the deuce court and the ad (Advantage) court. The deuce court is on the right side of the court for a player and this is where the ball is served into when the score reads 40-40 (deuce). The ad court is the side on the left and this is where the serve after deuce will be made. (The point after deuce is termed as advantage either to the server or receiver, whoever wins the point after deuce).
4. No man’s land: This is the area where a player is most vulnerable. It is a 486 sq feet land (18 x 27) between the service area and baseline.
5. Singles sideline: Only the doubles game is played on the entire court. 27 feet out of the 36 feet wide court is used for a singles game.
6. Doubles alley: The area between the doubles sideline and singles sideline is called the doubles alley or tramlines.
In addition to the above specifications, the surface of the court also plays a big role in how a tennis match unfolds. The speed with which the ball travels and the bounce of the ball depend on the surface on which the game is played.
Grass courts: These are generally fast. The games are very short due to the quickness and the low bounce. Wimbledon is played on grass courts.
Clay courts: Clay courts produce very high bounce compared with grass courts. The surface also slows down the ball. The French Open is played on clay, and Rafael Nadal is a claycourt master.
Hard courts: Hard courts are made of rigid synthetic material. The ball travels faster than clay on this surface but slower than grass, while the bounce is also somewhere in the middle. The US Open and Australian Open are played on hard courts.
