Overclocking processors is a reasonably simple task to perform, but it has a lot of side effects that need to be taken care of beforehand. It's not risky if you know what you're doing. The best CPUs on the market can still offer headroom, allowing them to squeeze in more performance.
The chip runs hotter and needs more power when you overclock the CPU. You need to ensure you don't have a stock CPU cooler that comes in the box, as they are not designed for overclocking.
You'll need a good-quality third-party cooler to keep the CPU cool and not let it thermal-throttle. Another thing you need to be sure is that your PSU can support extra wattage as an underpowered PSU can lead to shut-downs and cause damage to your components.
Before overclocking your CPU, you need to determine whether your CPU and motherboard support it. For Intel, overclocking is supported if your CPU has a "K" or "X" suffix in its name.
AMD processors have remained unlocked and overclockable for generations, including their latest Ryzen CPUs. Intel motherboards with the "Z" prefix are models that fully support overclocking. You can find out which CPU you have by pressing Win+Pause/Break.
How to overclock CPUs for gaming
You can start the process if you have an overclockable CPU that will not overheat, and the PSU can provide sufficient power.
For Intel, you need to download the Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU), which is a free software designed to overclock Intel CPU. Similarly for AMD, the AMD Ryzen Master software works well with overclocking AMD processors, and both the software have similar steps.
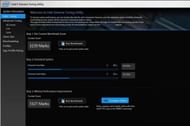
Under "Basic Tuning" in the XTU software, you'll see "Processor Core Ratio" and "Processor Cache Ratio" sliders. You need to increase both the sliders 1x each time and reboot your PC to see if it is stable with temperatures under control. Do not make drastic changes and keep both the sliders at roughly the same frequency.
You can move on to Advanced Tuning if you are sure about the changes you need to make. Under this tab, you'll find the Core Voltage and Processor Core Ratio per Individual Core.
CPU Voltage can be increased here as the CPU needs more power to overclock. Increase the Core Voltage Offset by 0.05V only once you increase the Processor Core and Cache Ratio to stay safe.
Run benchmarks after making changes each time and keep increasing the sliders until you reach your desired performance levels.
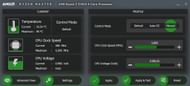
For AMD, you need to switch the Control Mode from "Default" to "Manual", which will allow you to adjust clock speeds and voltage. Similarly, you need to increase the CPU Clock Speed in increments of 50MHz and click on "Apply and Test". This software will boost your processor's frequency and test it.
Increasing the voltage is important, too, as it helps keep the CPU stable while overclocking, but it also increases the CPU temperatures. In the CPU Voltage section, keep increasing the voltage by 0.025V and test until you've reached the highest performance under stability.
Once you find a good combination of increased frequency and voltage, you have successfully overclocked your CPU. You need to run stress tests to ensure the PC stays stable under heavy loads for long periods and will not crash in the middle of a gaming session.
FurMark from Geeks3D is a recommended stress tester that will give you a good idea of your CPU's temperature at base frequencies and while overclocked.
